Which of the Following Affect the Chemical Composition of Seawater
Increases concentration of ions. D The chemical composition of seawater has great spatial variability.
Describe some of the biologically important properties of.

. A Seawater is pure water H20. Edited Dec 17 2018 at 2032. D Eighteen elements account for 75 of the dissolved.
Salinity decreases with depth Below 1000 m salinities are generally between 34 and 35 at all latitudes. Under water volcanic activity. Haloclinefrom the base of the mixed surface layer to about 1000 m depth At high latitudes.
The opposing influences of physical mixing and of biogeochemical input and removal mechanisms result in a substantial variety of chemical distributions in the oceans. For instance although seawater contains about 28 times more bicarbonate than river water the percentage of bicarbonate in seawater as a ratio of all dissolved ions is far lower than in river water. Describe some important properties of water.
However the ratios of solutes differ dramatically. Seawater generally has the pH of 75 to 84. Seawater is composed of about 86 oxygen 11 hydrogen and 3 of minerals consisting mainly of sodium and chlorine.
Increases concentration of ions. Salts dissolve in water washed into sea. Approximately 35 percent of seawater is composed of dissolved compounds while the other 965 percent is pure water.
Research during the past century has demonstrated that the composition of seawater is essentially uniform and that the relative proportions of the various ions are practically constant. Follow this question to receive notifications. A The chemical properties of seawater show very little latitudinal variability though some minor variability with depth.
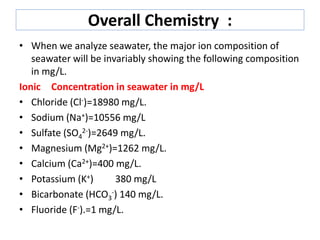
B The salinity of seawater is negligible. Because of the weathering of rocks salts dissolve in waterwashed into sea. Sodium Na Chloride Cl Magnesium Mg Potassium K Sulfate SO4 and Calcium Ca.
Salinity increases with depth At mid and low latitudes. Seawater contains more dissolved ions than all types of freshwater. As Neal said an increase in seawater temperature would lead to.
Explain how differences in evaporation and precipitation affect the salt content of the oceans. The chemical composition of seawater reflects such processes as erosion of rock and sediments volcanic activity gas exchange. For example at the same.
Seawater carbonate chemistry 12 Basic chemistry of carbon dioxide in seawater 121 Introduction Seawater is unique among natural waters in that its relative composition is well defi ned see eg. Salinity is the amount of dissolved solids in seawater Used for determining the density of seawater Affects the freezing point of seawater Affects the temperature of maximum density of seawater Changes in salinity drive thermohaline circulation Temperature and salinity characteristics fingerprint origin of water masses. As temperature increases water becomes less dense.
Many things like salts sugars acids bases and other organic molecules can be dissolved in water. In addition to water made up of hydrogen and oxygen atoms H 2 O seawater in the ocean has more than 70 elements dissolved in it but only six make up more than 99 of all the dissolved salts and all occur as ions that is electrically charged atoms or groups of atoms. 1 State and explain three factors that affect the chemical composition of sea water.
The concentration of dissolved oxygen in the surface water of open oceans ranges from 4mgdm-3 to 9mgdm-3. B Samples of ancient seawater suggest a great deal of chemical variation over the Earths history. List the main salts gases and nutrients in sea water.
In the open ocean the salinity approximately the total weight of dissolved solids per kilogram averages about 35 parts per thousand but may rise to 40 parts. The physical and chemical properties of seawater vary according to latitude depth nearness to land and input of fresh water. 23 plots correct 1.
Temperature salinity and pressure affect the density of seawater. Physical mixing in the oceans thermohaline and wind-driven circulation tends to homogenize the chemical composition of seawater. Release sulphate and chloride ions.
Cold water is denser than warm water with the same salinity. 4 plots correct 2. These differences in density are due to changes in either the salinity a measure of the dissolved salts in sea water or temperature.
Dissolve in sea waterrain water. Composition of Ocean Water. Water has oftentimes been referred to as the universal solvent because many things can dissolve in water Figure 144.
Seawater has the average density of 1025 kg per liter. Bicarbonate ions constitute 48 of river. Chemical analysis of seawater is the great way to deeply understand the chemical containment in the seawater.
Metals in dust make carbon dioxide to form bicarbonate. C Seawater contains dissolved gases suspended and dissolved organic matter and many trace elements. C Seawater is a solution.
As the temperature increases the bonds holding the protons are broken and the pH increases. We know that they are more dense than the pure water since seawater contain salt which improves the mass. There typically is a.
Millero et al 2008 and dominated 993 by mass by a fairly limited number of major ions Figure 11The various. Carbon dioxide to form bicarbonate. Under water volcanic activity.
Explain how volcanic activity affects the chemical composition of sea water Describe how temperature gradients form in water columns to produce ocean layers and how mixing of these layers may occur. Composition of Seawater 5 We now know that the currents studied by Marsigli are caused by differences in density of ocean water. State and explain three factors that affect the chemical composition of seawater.
Large water masses of different densities are important in the layering of the ocean water more dense water sinks. Tell how the animals and plants of the ocean affect the chemical composition of seawater.


Comments
Post a Comment